Keeping your data safe is more important than ever and understanding Data Leak Prevention vs. Data Loss Prevention is a crucial first step.
Whether you’re running a business or simply storing personal files, the last thing you want is to lose important information or have it fall into the wrong hands. Data leaks and data loss are two common threats , and while they might sound alike, they’re actually quite different. Understanding what sets them apart is the first step to keeping your information secure.
In this blog, we’ll explore what data leaks and data loss are, how they differ, and simple ways to prevent them.
What is a Data Leak?
A data leak occurs when sensitive information is unintentionally exposed to unauthorized parties through accidental sharing, weak security, or internal threats . Examples include misdirected emails, misconfigured cloud storage, lost or stolen devices, etc. Data leaks can drastically lead to reputation damage, legal issues, and financial loss which makes prevention strategies strong and essential.
What is Data Loss?
Data loss refers to the permanent disappearance of data due to activities such as accidental deletion, human error, or malicious activities. Unlike data leaks, where information is exposed but still accessible, data loss makes the data inaccessible and destroys the data.
Common scenarios include hardware failures such as hardware crashes, and malware attacks such as ransomware or viruses that erase the data. Software errors, such as bugs or compatibility issues, can also lead to corrupted files.
Key Differences between Data Leak and Data Loss
| Aspect | Data leak | Data loss |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unauthorized exposure of sensitive information to unintended parties. | Permanent or temporary disappearance of data. |
| Cause | Accidental sharing, weak security, or insider threats. | Accidental deletion, corruption, or malicious attacks. |
| Impact on data | Data is exposed but still accessible. | Data becomes inaccessible or destroyed. |
| Examples | Misdirected emails, misconfigured cloud storage, insider threats. | Hardware failure, malware attacks, accidental deletion. |
| Consequences | Privacy breaches, legal issues, and reputation damage. | Disrupted operations, financial loss, and compliance violations. |
| Intent | often unintentional but can be due to insider threats. | Usually accidental or caused by technical failures. |
| Detection | May be detected through security audits or unusual activity. | Detected when files are missing or corrupted. |
| Detection | May be detected through security audits or unusual activity. | Detected when files are missing or corrupted. |
| Legal Implications | May lead to lawsuits, fines, or regulatory penalties. | May result in compliance violations or business loss. |
Common Causes of Data Leak and Data Loss
There are multiple ways that data leaks and loss can happen.
Major Causes of Data Leaks

1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing is basically a trick where cybercriminals fool people into handing their sensitive data such as passwords, credit card details, or company data. Instead of hacking, they exploit human trust by pretending to be someone trustworthy. It can be a bank member, a government agency, etc.
How it Works:
Cybercriminals send emails, messages, or fake websites that portray something like legitimate organizations such as banks, agencies, etc. The recipient is tricked into clicking those malicious links and infected attachments. By doing so, they may unknowingly install malware and provide confidential information.
2. Weak Access Controls
Weak access controls happen when people have too much access or rights than they really need. This actually increases the chances of both accidental and malicious risks.
How it Works:
- Lack of proper role-based access control (RBAC) allows employees to access data unrelated to their job responsibilities.
- Failure to regularly review and update access permissions leaves former employees or irrelevant users with lingering access.
3. Insecure Third-Party Services
Organizations usually rely on third-party services, cloud platforms, or service providers for data storage or processing. If these services have weak protocols, they can become vulnerabilities.
How it Works:
- Third parties may store confidential information without any safety protocols which make it vulnerable.
- Lack of security audits of vendor systems can leave backdoors open.
- A data breach at the third-party provider can expose the data of multiple clients.
4. Human Error
Human error is the major cause of data leaks, often due to negligence, unintentional actions, poor security measures, and simple mistakes.
How it Works:
Misdirected Emails: Sending sensitive files to the wrong recipient.
Improper Data Handling: Not handling data properly such as uploading confidential data to public servers.
Weak Security Practices: Failing to use weak passwords, encryption, or two-factor authentication.
Unintentional Data Exposure: Accidentally posting sensitive data on the internet.
Causes of Data Loss
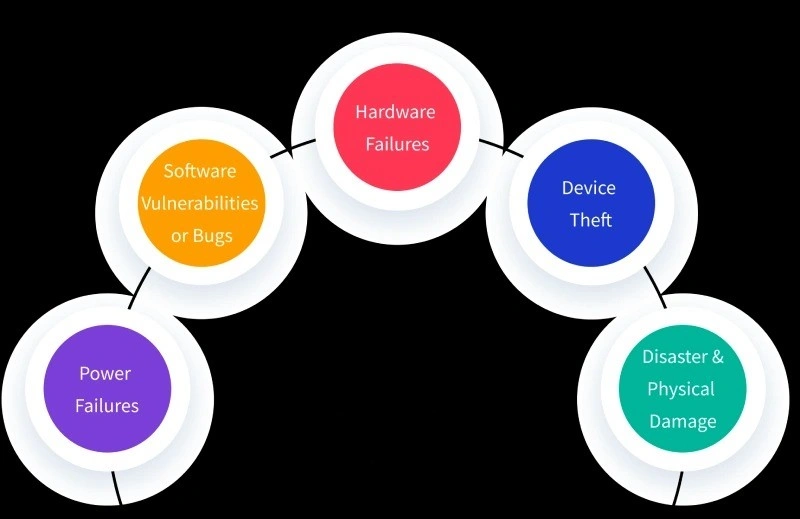
1. Power Failures
Unexpected power failures, sudden system crashes, or improper shutdowns can result in unsaved work being lost which cannot be retrieved back.
How it Works:
- When the system loses power all of a sudden, any unsaved changes in the RAM are lost.
- In-progress files may be interrupted, which results in incomplete or corrupted data.
- Power surges can damage storage devices, making the data irretrievable.
2. Software Vulnerabilities or Bugs
Flaws in software applications can lead to data loss . Additionally, ransomware and malware attacks exploit software vulnerabilities to encrypt, steal, or destroy data.
How it Works:
- Software Bugs: Glitches or programming errors can result in data inconsistencies or corruption.
- Ransomware: Malicious programs encrypt data and demand payment for decryption keys.
- Compatibility Issues: Running incompatible or outdated software versions can cause file corruption.
3. Hardware Failures
Storage devices such as hard drives, SSDs, and external storage failure can result in permanent loss of data.
How it Works:
- Mechanical Failures: Physical damage to moving parts in HDDs.
- Electrical Failures: Voltage fluctuations or power surges damaging storage components.
- Logical Failures: Corruption of file systems or bad sectors making data inaccessible.
4. Device Theft
If you lose a laptop, phone, or drive with important data, the information could be lost or shared if the device isn’t properly protected.
How it Works:
- Physical Theft: Devices are stolen during travel or from the workplace .
- Misplacement: Devices left behind in public spaces or lost in transit.
- No Encryption: If the device isn’t protected, it can be accessed by any individual
5. Disasters and Physical Damage
Natural disasters or accidental physical damage (fire, floods, earthquakes, or spills) can destroy data storage devices, making data recovery impossible.
How it Works:
- Fire or Water Damage: Physical destruction of servers, hard drives, or storage units. .
- Power Surges: Lightning strikes or electrical malfunctions frying storage devices.
- Structural Collapse: Earthquakes or explosions damaging entire data centers.
Strategies to Prevent Data Leaks and Data Loss
Data exposure is risky for both businesses and individuals. But don’t worry, there are practical strategies you can follow for data leak and loss prevention, keeping your information safe and secure.
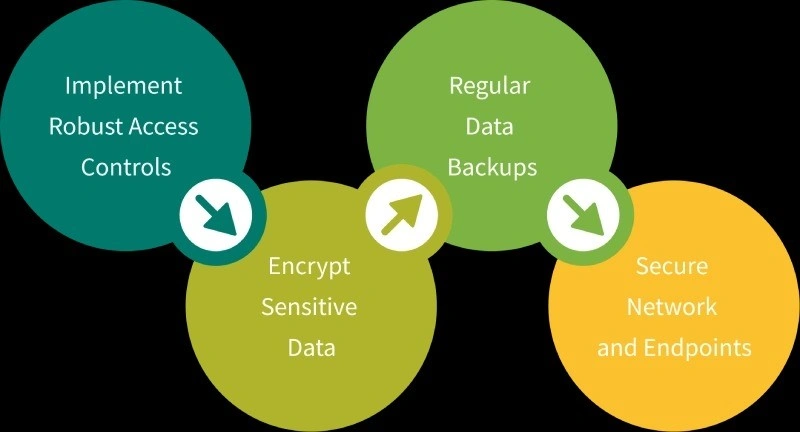
1. Implement Robust Access Controls
To prevent data exposure, it is better to use effective access controls. Implementing role-based access control ensures that employees can only access data that is relevant to their roles which reduces the risk of data. Giving people only the minimum access they need for their work reduces the risk of data misuse. To further improve security, companies should implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), adding an extra layer to security to security that makes it harder for attackers to gain access.
2. Encrypt Sensitive Data
Encryption plays a crucial role in protecting data from unauthorized access. By applying end-to-end encryption, companies can securely store data during transmission, preventing interception by third parties. When data is stored, using strong encryption like AES-256 makes sure that even if someone gets their hands on it, they can’t read it.
To keep the encryption effective, it’s important to regularly update the keys and manage them properly. This helps prevent hackers from cracking it with outdated or weak encryption.
3. Regular Data Backups
To avoid losing important data, companies should set up automatic and regular backups.
The 3-2-1 backup rule helps keep data safe:
- 3 copies of the data.
- Stored on 2 different types of storage (like a hard drive and cloud).
- 1 copy kept in another place.
It’s also important to check backups often to make sure they work properly. This way, if data is lost, it can be quickly restored with less trouble.
4. Secure Network and Endpoints
A safe internet is important to stop data breaches. Companies should use firewalls, IDS, and IPS to watch for and block any suspicious activity. For remote workers, using a VPN keeps data safe and secure while it is being sent, which makes it harder for hackers to steal. Protecting devices with antivirus, anti-malware, and security tools helps reduce risks and keeps the network secure from threats.
Best Practices for Data Protection
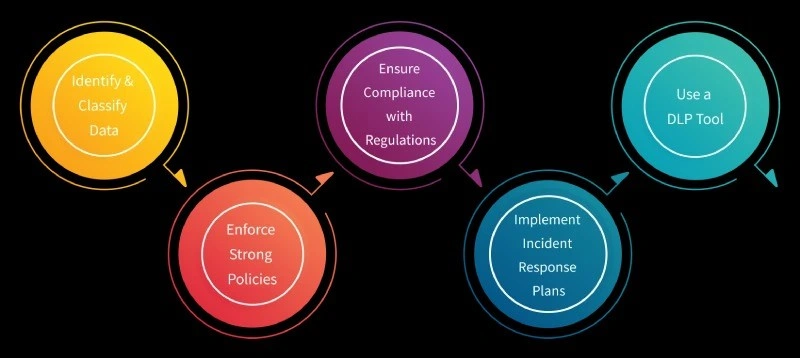
1. Identify and Classify Data
Identifying and classifying the data is the initial step in data protection . Companies should conduct data discovery and classification to label the information. By using appropriate security measures based on data sensitivity, such as encryption or restricted access, etc. Regularly reviewing and updating these policies makes sure that new types of data or changes in sensitivity are properly accounted for.
2. Enforce Strong Policies
To protect your data from various threats, it is important to store your data with strong passwords. Using complex, strong passwords helps to reduce the risk of data exposure. Using a password manager helps employees generate and store secure credentials which reduces the likelihood of weak passwords. Using multi-factor authentication strengthens security which makes it more difficult for attackers to gain access.
3. Ensure Compliance with Regulations
Conducting routine audits and assessments of security practices to ensure compliance and detect potential weaknesses. This enables you to comply with industry regulations and data protection standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, which contribute to the legal and ethical management of data. Maintaining detailed records of data handling and protection measures demonstrates transparency and accountability, which is crucial during audits or investigations.
4. Implement Incident Response Plans
A clearly defined incident response (IR) plan is a must to mitigate the impact of data breaches . It should define detection, containment, and recovery procedures to facilitate a swift and coordinated response. Conducting regular incident response drills helps employees to handle real-world incidents effectively which reduces downtime and limit damage during an actual breach.
5. Use a DLP Tool
A Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tool serves as the essential method to stop both unintentional and deliberate data leaks. It helps organizations detect unauthorized data transfers through sensitive information and enforces security policies. Tools like Time Champ help track suspicious activities, making it easier for companies to improve their data security. Using DLP on devices, networks, and cloud platforms helps reduce the risk of data breaches and ensures companies follow data protection laws.
How Time Champ Helps to Protect Your Data
Time Champ offers strong data protection features to help companies keep their information safe and boost productivity . With website blocking , companies can stop access to harmful or distracting sites, helping employees stay focused and follow company rules. It also tracks web activity in real time, giving insights into browsing habits. The USB device controls feature blocks external devices, like pen drives, to prevent unauthorized data transfers. It sends instant alerts and screenshots when a device is connected, allowing companies to act quickly and improve security.
Time Champ also tracks changes to files in real-time, helping companies quickly spot and stop unauthorized edits. This reduces the risk of data breaches. The attachment control feature prevents data leaks by blocking file uploads and downloads through emails and online platforms. It instantly detects security threats and protects sensitive information with encryption and automatic labeling. These features make Time Champ a helpful tool for protecting data, reducing risks, and following data protection rules.
In addition, Time Champ sends suspicious activity alerts by analyzing employee behavior, helping companies spot risks and respond quickly.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, data leak prevention and data loss prevention are crucial to avoid financial damage, legal issues, and loss of trust. By using strong security measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular backups, companies can reduce risks. Following simple safety rules, obeying data laws, and having a clear plan for handling problems make data protection stronger and keep the business safe and reliable.
Frequently Asked Questions
In simple words, a data leak is when private information is shared with people who shouldn’t see it, while data loss is when information is deleted or can’t be accessed.
Big time. Public Wi-Fi can be a playground for cybercriminals. If your team is remote or hybrid, a VPN is a must-have layer of defense.
Not testing them. A backup only helps if it actually works when you need it. Make sure you're regularly checking your restore points, so your recovery plan doesn’t fail when it matters most. /p>
Not always. If caught early, data recovery tools can help. But overwritten or corrupted files can be gone for good another reason why frequent backups are essential.







