What is Benchmarking?
Benchmarking is the process of comparing an organization’s processes, performance metrics, products, or services against those of industry leaders or best practices to identify areas for improvement. It involves analyzing key indicators such as cost, quality, speed, and efficiency to set goals, adopt best practices, and improve competitive advantage.
Benchmarking Procedures in HR
Identify Areas
The first thing in the benchmarking process involves identifying specific areas of HR that need to be improved or optimized. This could be from hiring, and employee recruitment to talent selection, staff engagement, training and staff performance management. The objective is to identify useful information that offers a perspective on how best-in-class HR processes work.
Select Benchmark Tools
Once these areas have been identified, the next step is a selection of benchmarking tools. These tools may be surveys, performance metrics, and reports from the industry or even collaborating directly with other organizations.
Compare and Analyze Data
Organizations can use the established benchmark tools to compare their HR practices against competitors or industry experts. The analysis contains key performance indicators, efficiency metrics, as well as qualitative aspects of HR functions.
Implement and Improve
Use the reviewed data to test new methods and plans to improve your results. Doing this every six months helps you follow market trends and stay ahead of the competition.
Different Types of Benchmarking
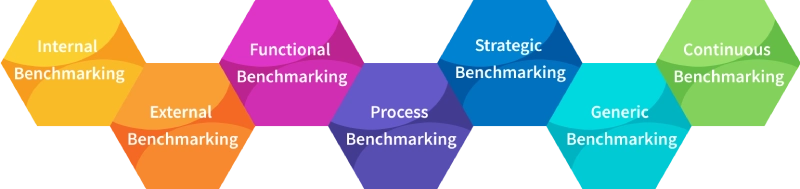
Internal Benchmarking
Internal benchmarking involves the internal comparison of different departments or teams within the same organization. This actually helps to identify which teams or departments need additional resources or support. It is helpful for large organizations that handle various independent departments.
External Benchmarking
Competitive benchmarking is a strategic approach where you compare the team’s position to its competitors. This technique reveals the organization’s place in the market and identifies areas to strengthen its competitive position.
Functional Benchmarking
Functional benchmarking lets you compare similar functions in your organization with those in another. It helps you see how your team’s strategies compare to others and stay updated on trends. For example, a company might use functional benchmarking to compare its marketing strategies with those of a successful competitor.
Process Benchmarking
Process Benchmarking refers to the practice of comparing specific processes or workflows within an organization to similar processes in other organizations, typically industry leaders or best-in-class performers. The purpose is to find best practices, learn about the strategies of leaders in the field, and implement changes to increase effectiveness, productivity, and quality in organizational activities.
Strategic Benchmarking
Strategic benchmarking involves identifying best practices and successful strategies of top companies and incorporating those approaches into your own operations. This benchmarking looks beyond your industry, taking ideas from other sectors.
Generic Benchmarking
Generic benchmarking is the process of comparing your organization’s practices and performance with those of top-performing organizations from any industry to identify and adopt effective methods for improvement. This approach helps you focus on general best practices and think about how to apply your organization’s values across teams and processes. It gives a broad overview of business practices and helps you understand how your team works compared to others.
Continuous Benchmarking
Continuous benchmarking shows the need for constant evaluation and enhancement. Instead of carrying out benchmarking as a once-in-lifetime activity, you should continuously track performance metrics, follow industry patterns and revise your practices accordingly. This approach makes the organization agile and adaptable in a business environment that is constantly changing.
Benchmarking Examples
Benchmarking is all about learning from the best to improve. For example, a store might learn from how Amazon delivers quickly, a hospital could use airline schedules as a guide to shorten wait times, and schools might copy good teaching ideas from the best schools. Tech companies usually compare how competitors use tools like cloud computing, and athletes or sports teams learn from the training routines of top performers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Robert C. Camp is known as the creator of benchmarking. In the 1980s, he led benchmarking at Xerox and helped develop the practice.
No, benchmarking works for small and big businesses alike. Small and medium-sized businesses can also gain from comparing their practices and performance with top companies to improve efficiency and stay competitive.
Common problems include finding similar data, facing resistance to change in the company, and spending time to understand and apply benchmarking results.





