What is a Financial Incentive?
Financial incentives are rewards and benefits that are provided to inspire individuals or groups to complete a specific task, reach certain goals, or perform at the required level. Such rewards are most often monetary in form, e.g. bonus, commission, profit-sharing, or performance-based pay. Financial incentives are the most common way for organizations to motivate their staff to achieve desired behaviour, improve performance, increase productivity, and drive results. These can also be implemented to attract and retain talents; align individual and organizational goals; and promote performance culture and accountability.
Types of Financial Incentives
- Bonuses: Bonuses are one-time payments awarded to employees for achieving predetermined goals, such as meeting sales targets, exceeding performance expectations, or contributing to company profitability.
- Commissions: Commissions are payments made to employees based on the sales or revenue they generate. Sales representatives, for example, may receive a commission as a percentage of the total sales they close.
- Profit-sharing: Profit-sharing programs distribute a portion of the company’s profits to employees. This incentivizes employees to contribute to the company’s success and aligns their interests with those of the organization.
- Stock Options: Stock options give employees the right to purchase company stock at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. This allows employees to share in the company’s growth and success, as the value of the stock increases over time.
- Performance-Based Pay: Performance-based pay ties compensation directly to individual or team performance. Employees receive pay increases or bonuses based on their achievement of specific performance goals or objectives.
- Merit Pay Increases: Merit pay increases are salary increases awarded to employees based on their individual performance, contributions, and accomplishments. These increases are typically given on an annual basis and are intended to reward top performers.
- Recognition Awards: Recognition awards, such as employee of the month or peer-nominated awards, provide public acknowledgement and appreciation for outstanding performance or achievements. While not always strictly financial, they can include monetary rewards or other incentives.
- Signing Bonuses: Signing bonuses are lump-sum payments offered to new employees as an incentive to join the organization. These bonuses are typically paid upfront upon signing an employment contract.
- Retention Bonuses: Retention bonuses are payments made to employees to encourage them to stay with the organization for a specified period. These bonuses are often used to retain key talent or employees with critical skills or experience.
- Referral Bonuses: Referral bonuses are rewards given to employees who refer qualified candidates for open positions within the organization. This incentivizes employees to help recruit top talent and can help reduce recruitment costs.
What are Non-Financial Incentives?
Non-financial incentives are things you get at work that aren’t money. Instead, they make you feel good or help you in other ways. They might make you happy or help you work better. These perks are used to make employees feel valued and happy at work and to make the workplace a nice and friendly place to be.
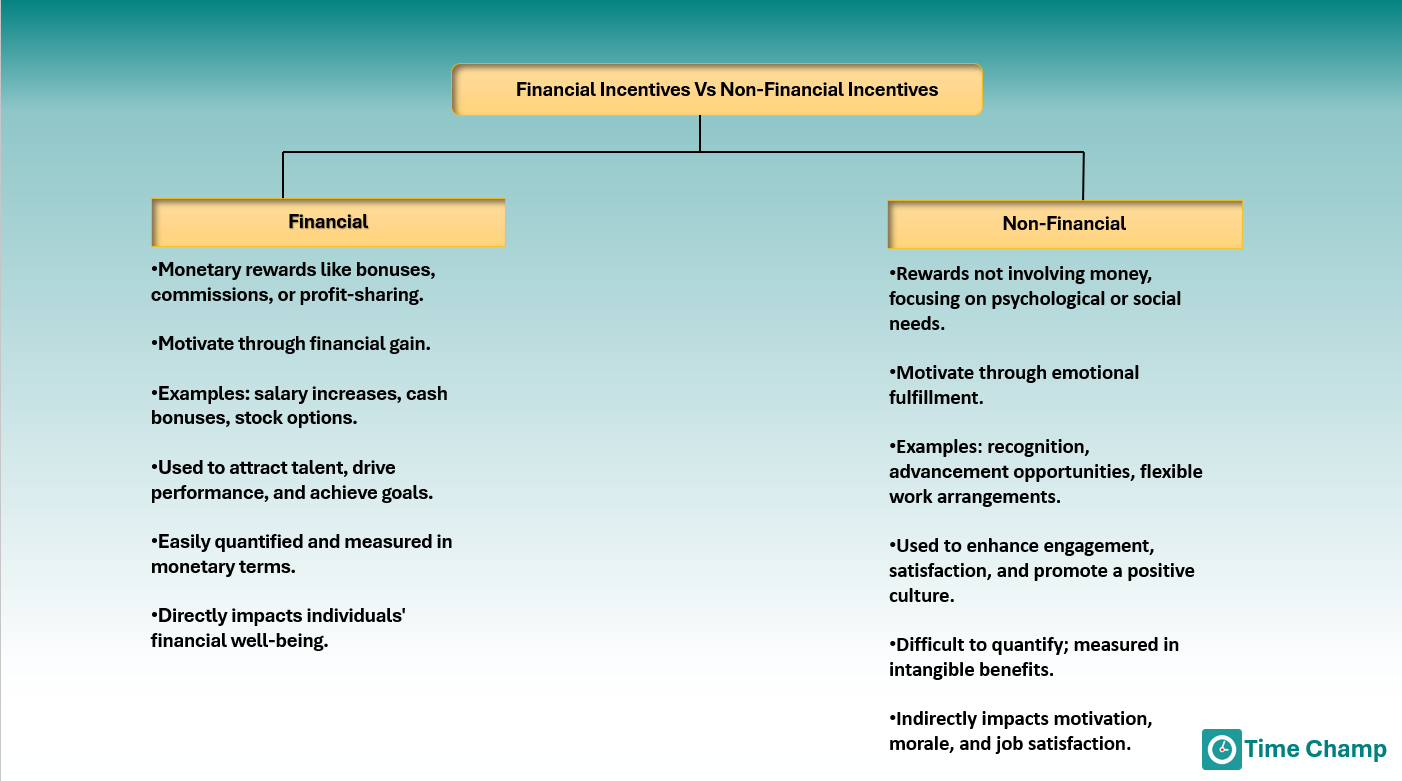
Difference between Financial and Non-financial Incentives
Boost your team’s motivation and achieve great results with the right rewards. Let Time Champ help you keep track of progress and measure success. Sign up now for a demo and make sure your incentives match your company’s goals with Time Champ.
People also look for
What is Stipend? Meaning & Definition
Employee Appreciation Email for their Good Performance
What is Gratuity Meaning? & Definition
FAQs
Financial incentives are monetary rewards given to employees to encourage specific behaviors, enhance performance, and align their goals with those of the organization.
Yes, financial incentives can significantly boost employee motivation by providing tangible rewards for achieving certain objectives.
Common financial incentives include bonuses, commissions, profit-sharing, stock options, performance-based pay, merit increases, recognition awards, signing bonuses, retention bonuses, and referral bonuses.
The effectiveness of financial incentives can vary depending on the company culture, the nature of the work, and the personal values of employees. They are generally more effective in results-driven environments.

