Home / N / Non-Taxable Allowances
Non-Taxable Allowances: Definition, Types & Benefits [2025]
Non-taxable allowances are an important part of payroll structures that can effectively reduce tax liabilities. Non-taxable allowances are special allowances provided by employers for a specific purpose (house rent, travel, medical, etc.) and are exempt from income tax totally in some cases or to some limits in other cases. A clear understanding of these allowances makes it much easier to plan finances and make more effective use of income without paying excess tax.
These different types of non-taxable allowances are largely varied and deal with issues related to supporting employees to perform their roles and functions. All types of employees receive allowances every so often. Where do you want to go, and which tax tables apply? Non-taxable allowances that you may be familiar with include House Rent Allowance (HRA), Leave Travel Allowance (LTA), medical allowances, etc. However, some allowances are exempted totally in law, and some are exempted to a limit, so being clear on the difference in allowances helps employees take advantage of savings while keeping themselves from getting mixed up while filing their taxes.
Non-taxable allowances provide selected benefits beyond the basic tax reduction value. Non-taxable allowances help achieve financial assistance for what are often deemed essential needs, enhance employee take-home pay, and contribute to overall well-being. Non-taxable allowances can have important salary management purposes, as non-taxable allowances in 2025 have more value, provided salary and functional processes are understood for less taxable income, or in gaining resources to cover costs, or even allow for a better work-life application when delivered correctly.
What is Non-Taxable Allowance?
A non-taxable allowance is a fixed benefit from an employer that compensates for certain expenses that are considered non-taxable in whole or in part. Non-taxable allowances will reduce the amount of taxpayer income, meaning they provide a financial injection for the same defined purpose.
Non-taxable allowances are intended as a form of relief towards costs of payment associated with employment or personal well-being. For example, travel expenses, medical expenses, or educational purposes allowances are typically non-taxable. Whether any specific non-taxable allowance is taxed will depend on the nature of the allowance and the prescribed rules from the tax authorities.
Non-taxable allowances are not added to the taxable salary as taxable allowances are; therefore, they are an effective means to ensure you get maximum income. Non-taxable allowances are also key to balancing costs detached from work that would have been incurred by the employee in some capacity.
Employees should also learn which allowances are considered non-taxable to assist with future decision-making. Non-taxable allowances improve take-home pay and make the business operate under tax laws. With greater understanding, it reduces the chances of error when filing a tax return, and they will know how they can save tax efficiently.
What are Fully Exempt Allowances?
Fully exempt allowances are payments made by an employer to an employee that are never taxed. The amounts received under these categories of allowances are fully tax-exempt. Fully exempt allowances are provided without limit or any conditions. They remain tax-free and do not form part of total income. They are designed to provide total relief to employees for specific costs that the government recognises as necessary in some way.
These allowances are generally disbursed for certain circumstances, such as travel outside Canada, working with international organisations like the UNO, or upon certain benefits conferred under the judges of the High Court and Supreme Court. Since the allowances are explicitly exempted from income, employees will not need to include this amount in taxable income when filing income tax returns.
In other words, whatever you receive in this category, you are entitled to keep the whole amount, without tax taken off. Below are the examples of fully exempt allowances:
- Foreign Allowance: Any allowance, paid for any reason, by the Indian government to its employees posted abroad, is exempt from tax. The exemption was designed to ensure that someone working for the Indian government and costing more money because they are working abroad.
- UNO Allowance: Allowances paid to employees of the United Nations Organisation (UNO) are exempt from income tax in India. Such employees work with international bodies, and taxation may contradict international treaties.
- Judges Allowance: Allowance paid to judges of the Delhi High Court and Supreme Court is exempt from tax. The private nature of the allowances was introduced to respect the sacred position of judges and to ensure that their salary was not taxed.
These allowances represent a unique form of exemption to assist a unique professional environment, to ensure that employees are supported where there may be no tax burden.
What are the Types of Non-Taxable Allowances?
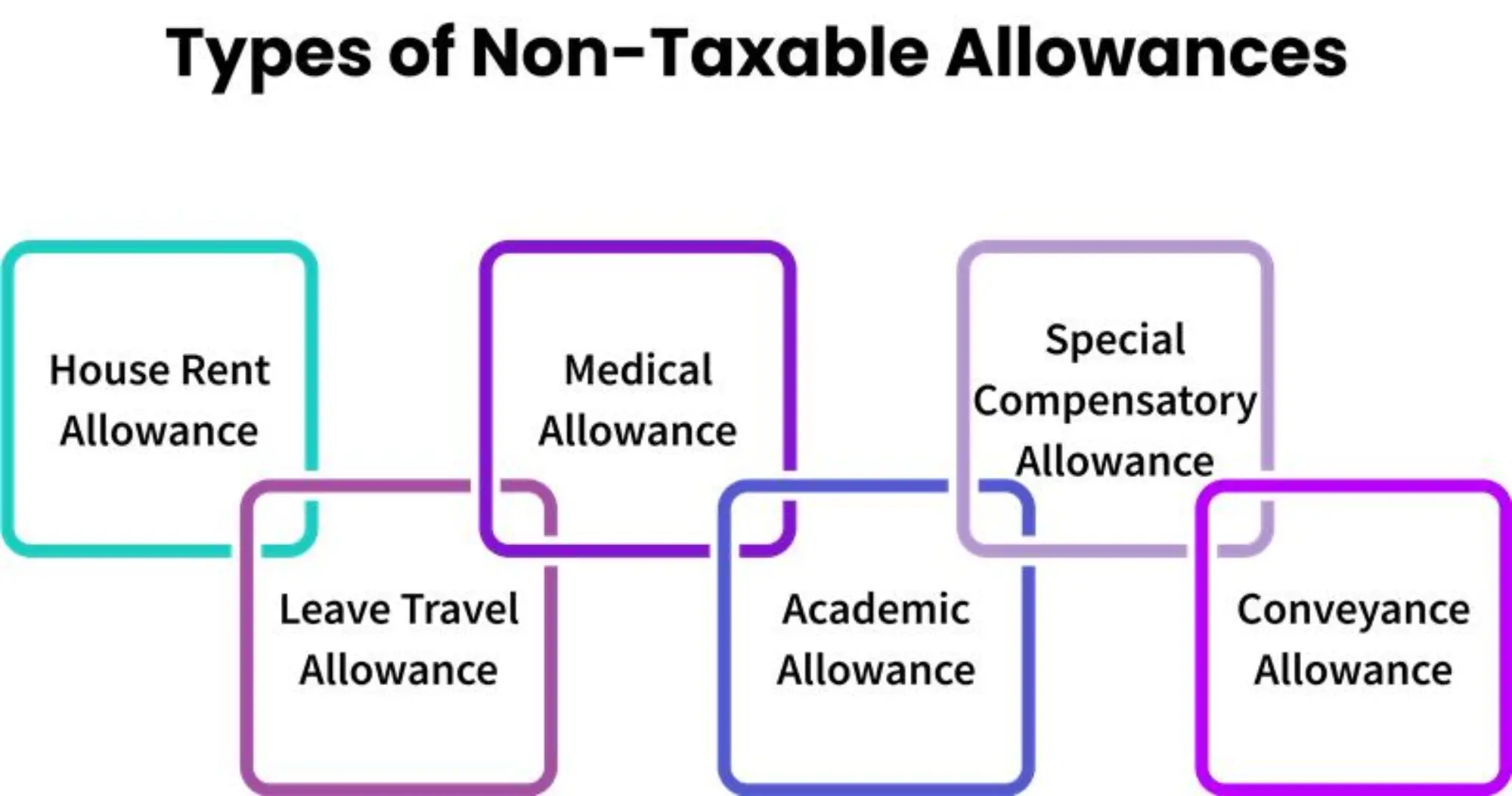
1. House Rent Allowance (HRA): HRA is one of the most prevalent tax-free allowances. HRA brings relief to employees who pay rent for the accommodation they live in. The exemption depends on the salaries drawn, rent paid, and the location of residence.
2. Leave Travel Allowance (LTA): Eligible LTA includes the cost of traveling to occur while on vacation within/around India. The exemption allowed for the eligible LTA is for the actual travel costs incurred while on vacation, and certain journeys may be claimed generally once in four years
3. Medical Allowance: Medical allowance significantly helps with employees' medical expenses as well as their families. Even with the prescribed limit, it still provides substantial relief towards employees' healthcare expenditure.
4. Research/Academic Allowance: This allowance is for employees who are engaged in research or academic work. As long as an employee spends their allowance according to its purpose, such as books or undertaking a project, it is tax-free.
5. Special Compensatory Allowance: This allowance is for employees who work in hard territories such as hilly, border, or remote places. This is a fully or partially tax-exempt allowance as per government regulations.
6. Transport/Conveyance Allowance: This allowance covers the cost of transport from home to the office. You can be exempt from transport/conveyance allowance up to a certain amount, and there is more exemption for disabled employees.
What are the Benefits of Non-Taxable Allowances?
1. Decreases Taxable Income: The most obvious benefit of non-taxable allowances is decreasing the taxable portion of income. This directly enables employees to pay less tax and save money while being fully compliant within the constraints of tax regulations.
2. Provides Financial Assistance: Allowances, like HRA, medical, or travel allowances, provide financial assistance, as they are intended for expenses that the employee would otherwise have incurred out-of-pocket. It also provides better effectiveness in providing an income for employee utilization more purposefully and effectively.
3. Motivates Work-Life Balance: Some allowances, for example, leave travel allowances, education allowances, and other personal benefits, ensure employees can invest in their personal development and leisure, can ensure an employee has the balance between the work they perform and the personal wellbeing of each individual.
4. Promotes Employee Retention: When companies provide non-taxable allowances, it gives employees a financial incentive to stay with the company. Allowances will benefit employees and contribute to employee retention as they increase employee satisfaction and loyalty at work, which reduces attrition.
5. Enhances Job Satisfaction: Employees feel great appreciation when an employer financially assists them via allowances. The increases the state of employee morale, engagement, and ultimately motivation and performance at work.
6. Assists with Financial Planning: Non-taxable allowances offered to employees allow them to better plan the management of their income and expense ratios. Employees are more effective at managing their finances when their employer covers or provides subsidies for certain costs.
7. Increases Productivity: By reducing employees' financial stress and getting them to manage more effectively by utilizing non-taxable allowances, employees can concentrate better at work, which ultimately leads to a boost in productivity at work overall.
What are the Tax Rules and Exemptions for Non-Taxable Allowances?
Tax Rules
Tax rules for allowances are all about deciding if the money received makes that property taxable or exempt. These regulations also clarify that the personal allowance exemption includes the allowance in salary income.
- Part of Salary: Allowances fall into the category of salary under the Income Tax Act legislation, but the decision on taxability is contingent on the categories of allowances received.
- Three Types of Allowances: An allowance can be exempt/completely exempt/partially exempt/fully taxable, and each classification comes with varying tax purposes and specifics as per the law.
- Proof: Employees are required to demonstrate proof for claimed (exempt) allowance via valid documents such as rent receipts for HRA, and travel tickets for LTA.
- Incorporated in Income Tax Return: All allowances must be properly incorporated while in the process of filing income tax returns for the taxpayers to ensure allowances claimed are appropriate exemptions.
- Employers' Role: The usual process is that employers will calculate the exemption at the source. However, when the employee or taxpayer is filing their return, they must ensure that their exemptions are correct and allowable.
Exemptions for Non-Taxable Allowances
Exemption means that employees do not have to pay tax on some or all of certain allowances that they receive from their employer. In India, tax exemption laws are contained in the Income Tax Act and were introduced to address concerns relating to income taxation, which allows the employee to satisfy working and personal needs.
- Fully Exempt: Some allowances have special or complete exemptions for taxation, for example, foreign allowances, UNO allowances, or allowances paid to High Court and Supreme Court judges.
- Limit Exempt: Some allowances are tax exempt up to a specified limit, such as house rent allowance (HRA), leave travel allowance (LTA), or children's education allowances.
- Partially Exempt: Certain allowances are partially exempt, such as HRA to the extent of a certain limit, which varies based on rent payable, basic salary , and the location of the employee.
- Taxability of Excess: If the allowance received is more than the exempt limit, only the excess is included in your income and taxed. The portion within the limit remains tax-free.
- Employee Benefit: The exemptions are intended to relieve the employee of the tax burden, and the reason the excess is taxed is that the employee will still be able to benefit from the allowance exempted from tax.
How do Non-Taxable Allowances Differ from Taxable Allowances?
Non-taxable and taxable allowances may appear similar because they are both a part of salary, but they differ in tax treatment. Non-taxable allowances give tax relief, and taxable allowances add to income and do not carry exemptions.
| Aspect | Non-Taxable Allowance | Taxable Allowance |
|---|

