Fixed pay, or fixed salary or fixed compensation, is the guaranteed part of a fixed employee’s salary that has to be the same every month. The components of fixed pay include basic salary, HRA, DA, PF, and other fixed allowances. Fixed pay does not depend on performance or business outcomes, so it provides financial certainty and predictability.
Fixed Pay usually consists of the basic salary, house rent allowance, dearness allowance, conveyance, medical allowance, and employer expenses such as PF. The computation of fixed pay is simply summing all these fixed elements. And of course, since bonuses, incentives, and commissions are variable, they do not count in fixed pay. When everyone has a clear salary structure, it helps create better planning for employees and employers.
Fixed pay has pros and cons. It supports trust, assists in financial planning, and provides job satisfaction. On the other hand, it will reduce motivation because it is not performance-linked. Knowing that fixed pay is guaranteed is different from knowing that variable pay is based on performance or profits from the business. Fixed pay and variable pay are part of a pay structure that provides stability for the employee and incentive for work effort.
What is Fixed Pay?
Fixed pay, sometimes called fixed salary or fixed compensation, is the part of your salary that stays the same every month and is guaranteed. It includes elements such as your basic salary, HRA, DA, PF, and several other allowances. Because it is consistent, it gives employees stability and security for the amount of money they will receive.
Fixed pay is valuable to employees because it guarantees a reliable source of pay. When you know exactly how much will go into your bank account every month, it makes handling expenses, saving money, and investing less difficult. Stability encourages employees to stay with the same employer.
Fixed pay is important because it provides financial stability for employees, helping them plan expenses, savings, and investments with confidence. It builds trust, loyalty, and job satisfaction as employees feel secure knowing their income won’t fluctuate with market conditions. For employers, fixed pay ensures predictable salary expenses, making budgeting easier and reducing the risk of overspending. It also helps attract skilled professionals by offering a reliable and steady income compared to variable pay structures.
What are the Components of Fixed Salary?
Fixed salary encompasses both your basic salary and the total of fixed allowances and contributions, which are fixed every month. It includes basic pay plus fixed allowances and contributions to be paid by the employer. Below are the major components of a fixed salary:
1. Basic Salary
This is the primary salary and makes up approximately 40–50% of the employee's overall fixed salary. A lot of dependent allowances like HRA, PF, etc, are calculated based on this salary amount.
2. House Rent Allowance (HRA)
HRA is an allowance paid to employees living in rented houses or accommodations, which, to some extent, may help with the borrowed costs of the house, and has tax benefits. The percentage of the HRA differs based on whether the employee is living in a metro area or not.
3. Dearness Allowance (DA)
Dearness Allowance is an additional income given to employees to assist in coping with the increasing cost of living. This is common to government and public sector jobs, which require the employees' salaries to be adjusted for rising prices. The salary cannot easily be changed multiple times in a year, so by adding DA, it helps individuals adjust their income due to inflation, making it easier to manage monthly expenses.
4. Conveyance Allowance
This is a small, fixed amount meant to assist employees in non-claimable daily travel between homes and workplaces. While it is considered small, it is somewhat of a regularised component in a lot of salary pieces.
5. Medical Allowance
Certain businesses also allow and help employees spend on health and medical expenses via a cash medical allowance each month. This allowance efficiently helps the employee budget the costs of regular medical expenses without the financial impediment.
6. Provident Fund (PF) Contribution
The employer deposits a percentage of your wage into your contribution to the Employee Provident Fund (EPF). This contribution typically comes directly from your wage packet every month, making it part of your fixed pay and allowing all employees to save for the future, so good news!
7. Special or Other Allowances
Along with the basic components stated above, some companies can also offer various other allowances, such as education allowance, city compensatory allowance, or special allowance, as part of the fixed wage. This is in accordance with a company policy and the employee designation.
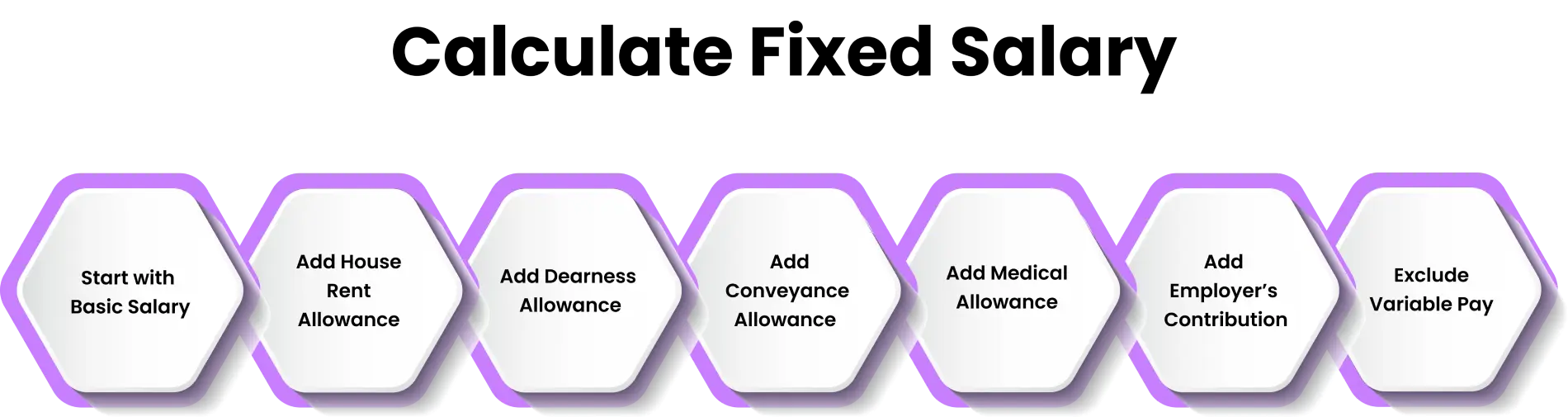
How to Calculate Fixed Salary?
Fixed salary is the amount that an employee receives every month without any changes. Fixed salary includes basic salary and allowances that are fixed. Understand the calculations in a step-by-step process in a very simple way.
Fixed Salary=Basic Salary+HRA+DA+Conveyance Allowance+Medical Allowance+Employer’s PF Contribution+Other Fixed Allowances
Step 1: Start with Basic Salary
Basic salary is the main part of fixed pay. It usually forms 40–50% of your total
salary.
Example: If your monthly salary is ₹60,000, then your basic salary could be
₹25,000–₹30,000.
Step 2: Add House Rent Allowance (HRA)
If you live in a rented house, companies usually give you HRA. The amount depends on your
basic salary and the city
you live in.
Example: HRA may be 40% of basic in non-metro cities and 50% in metro cities.
Step 3: Add Dearness Allowance (DA)
DA is given to balance the effect of inflation. It ensures your salary value is not reduced due to rising prices. Government and PSU jobs mostly have DA as part of the salary.
Step 4: Add Conveyance Allowance
Conveyance allowance is a common fixed amount reimbursed to employees who travel to their daily workspace. It is a small provision of the total remuneration structure. It is a small but important part of the salary structure, as it reduces the personal burden and ensures employees can travel to work without financial stress.
Step 5: Add Medical Allowance
Some companies give a medical allowance to help cover basic health-related expenses. Medical allowance is an amount that helps employees defray basic personal healthcare needs, whether that be regular health check-ups, purchasing their regular medicines, or visiting the doctor.
Step 6: Add Employer’s Contribution (PF & Gratuity)
Companies contribute to your provident fund (PF) every month. This is also counted in fixed pay. Some employers also include gratuity in the fixed pay structure.
Step 7: Exclude Variable Pay
Now, remember to remove anything that is not fixed. For example, bonuses , performance incentives, overtime pay, sales commissions, or profit-sharing are not included in the fixed salary.
Example:
- Basic Salary = ₹30,000
- HRA = ₹15,000
- DA = ₹5,000
- Conveyance = ₹2,000
- Medical Allowance = ₹3,000
- Employer PF Contribution = ₹3,600
Fixed Pay = 30,000 + 15,000 + 5,000 + 2,000 + 3,000 + 3,600 = ₹58,600
What are the Pros and Cons of Fixed Pay?
Fixed pay has its advantages and disadvantages. It provides stability for employees in knowing exactly what their monthly income will be, which helps with expense and savings planning. It gives employers predictability for budgeting and perhaps builds a level of trust with employees. But, since it does not change with performance, sometimes motivation is reduced, and it limits earning opportunities.
| Pros of Fixed Pay | Cons of Fixed Pay |
|---|
What is the Difference Between Fixed Pay and Variable Pay?
Fixed pay is the pay portion of an employee’s salary that is guaranteed and is consistent every month, i.e., basic pay, HRA, DA, allowances, etc. The variable pay portion is dependent upon performance against target and company results and can vary from time to time. Fixed pay provides employees with certainty of income, whereas variable pay provides an incentive to perform better and achieve targets.
| Fixed Pay | Variable Pay |
|---|

