Home / B / Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Definition, Steps & Examples
In the modern world of business, it is important to be ready to meet disruptions. Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is a means through which organizations learn the ways in which the operations can be disrupted by an interruption, such as a system failure, supply chain problems, or a pandemic. Categorizing vital operations and calculating possible losses, the leaders can have a proper plan on how to defend their organization.
A BIA is not only a recovery exercise, but a resilience process. It discloses the dependencies, priority of recovery, as well as the resource requirements. Consequently, teams would develop superior restoration plans and diminish downtimes.
It does not matter whether it is a natural disaster or a cyberattack, as long as you know what to expect in advance, your decision-making process will become more efficient, and your response time will be shorter.
What is Business Impact Analysis (BIA)?
Business Impact Analysis is a logical procedure in which the operational and financial impact of a disturbance to major business operations is assessed. It assists in establishing priorities of recovery, acceptable outage, and resources required on the basis of probable impact.
A BIA, which is also called Business Impact Assessment, is conducted at the beginning of the business continuity planning. It aims at determining the impact of an interruption on the revenue, customer satisfaction , compliance, and reputation. Such information is vital in helping the leaders to decide what systems should be restored first in a crisis.
The aim and significance of BIA consist in the determination of:
- What are the most important business functions?
- How much disruption can it withstand?
- Maximum offline time of operations
- What resources and healing methods are necessary
A BIA enables continuity planning to be based on reality because it plots interdependencies and ranks processes to provide a basis upon which continuity planning should be established.
How to Conduct a Business Impact Analysis (BIA)?
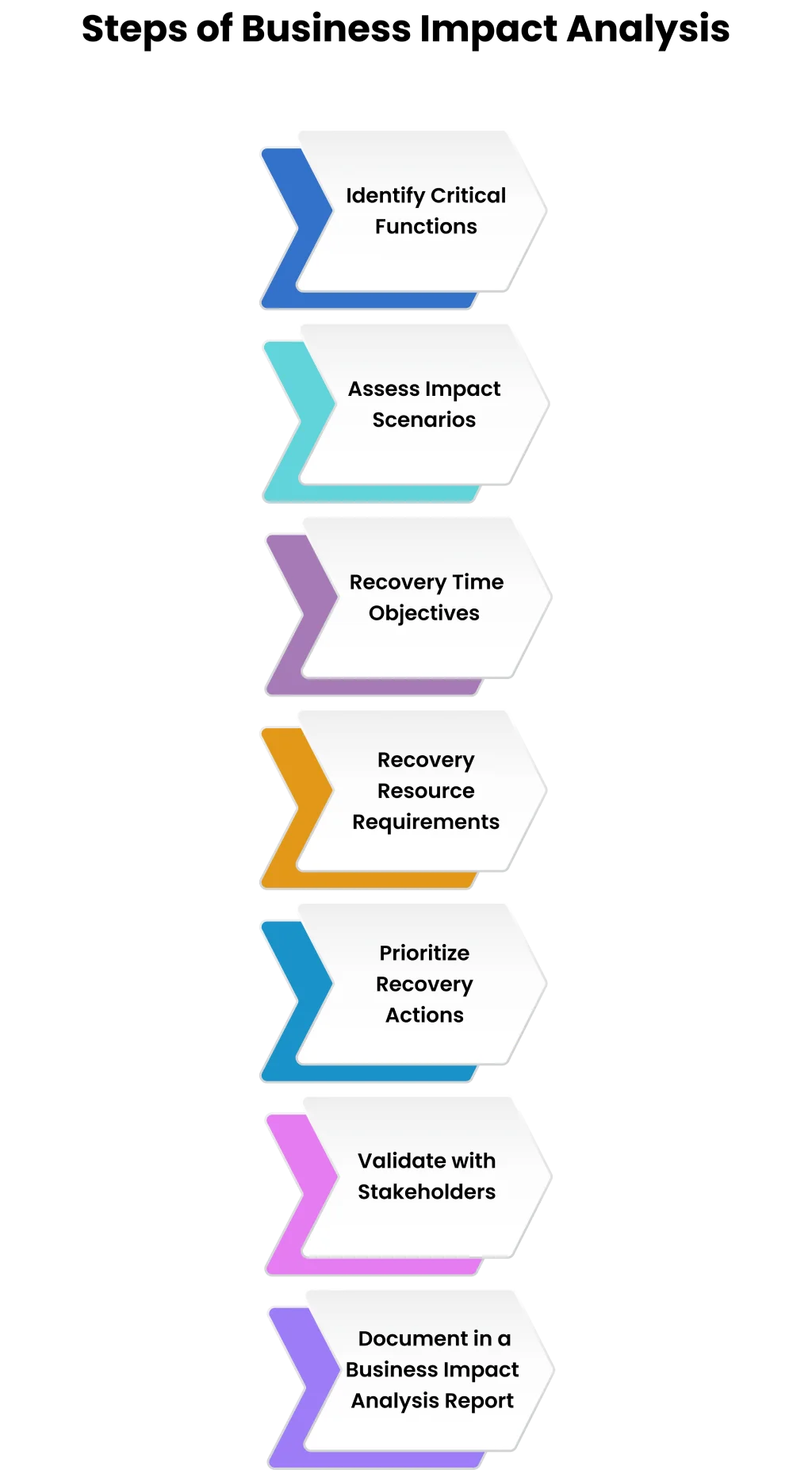
- Step 1: Identify Critical Functions: Begin by drawing a list of business processes and activities. Resort to department heads to establish critical functions, such as payroll, customer support, network operations, or supply chain logistics, then prioritize these functions.
- Step 2: Assess Impact Scenarios: Consider the operational, financial, legal, and reputational impact of disruption in each of the functions, such as estimated loss of revenue per hour, regulatory fines, or customer turnover.
- Step 3: Determine Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs): There should be an acceptable downtime level per critical function. Other systems may need a complete recovery of 1 hour, whereas some systems may need a recovery of 24 hours.
- Step 4: Define Recovery Resource Requirements: Determine tools, human resources, backup data , and access to information on the external vendors to restore each of the functions within a specified RTO. These are the framework of recovery plans.
- Step 5: Prioritize Recovery Actions: The ranking is done on the basis of urgency and impact. Priority functions must be given the first hand in recovery strategies.
- Step 6: Validate with Stakeholders: Summary of the analysis with department heads and risk teams. Ensure expectations, and schedules.
- Step 7: Document in a Business Impact Analysis Report: Put the findings, RTOs, dependencies, resource requirements, and recovery priorities into a single document that is ready to be used by the decision-makers.
What Are the Benefits of Business Impact Analysis?
A business impact analysis (BIA) is strategically clear, operationally resilient, and long-term growing. BIA generates value in the following ways, whether you are a large organization or a startup.
Better Risk Preparedness
The most vulnerable systems and processes will be identified in a BIA. This will ensure that mitigation plans are put in place by teams before risks become crisis.
Better Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
Any good continuity plan is based on BIA. Recovery operations can be prioritized and downtimes during disasters minimized by determining which business functions are of extreme importance.
Financial Loss Prevention
In full view of the impacts that disruptions have on revenue, operations, and compliance, businesses can invest resources effectively to avoid significant financial losses.
Alignment of Regulatory and Compliance
Most industries involve formal assessments. BIA is a complete approach that also allows businesses to remain in accordance with any regulations and compliance needs , like ISO 22301 or HIPAA.
Communication and Transparency in Operation
BIA also adds transparency between departments, as each team may see how their working processes affect the final purposes of the business.
More Rapid Decision Making in Disruption
Having critical information already mapped, the leadership can make well-informed, confident decisions at the time of the utmost response time.
What are the Examples of Business Impact Analysis (BIA)?
The example use case of business impact analysis can be used to demonstrate that:
- A software company will estimate the amount of money they lose per hour in case their customer portal goes down and then establish stringent recovery windows based on the information.
- A hospital considers the effect of the loss of access to patient records and establishes RTOs to make sure that clinical care will not be disrupted.
- A production company calculates delays in the supply chains and simulates the effect of a stop in production on the contract and the delivery of products to the clients.
- A retail chain has estimated the loss of revenue caused by point-of-sale failure and prioritized recovery of checkout systems and inventory tracking.
These cases demonstrate that a BIA puts clear business continuity priorities and resource plans in place.
What Should Be Included in a Business Impact Analysis Report?
An effective BIA report is written in a business impact assessment template, consisting of:
- High-level findings in the executive summary
- Critical business functions list
- Financial, operational, and reputational impact of scenario-based analysis
- RTO and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) of each functional role
- Staff (resources), systems, vendors, requirements
- Dependencies and backup plans
- Suggested sequence of recovery with reasons
- Stakeholder checks and reviews the history of documents
What is the difference between a BCP and a BIA?
Although these are related, Business Continuity Planning (BCP) and Business Impact Analysis are not the same:
BIA assesses impact and determines recovery priorities using risk and acceptable downtimes.
BCP incorporates action plans, procedures, and backup strategies using the results of the BIA.
Concisely, BIA is the analytical framework. BCP is the implementation strategy that is anchored on that.

