Salaried employees are those who earn a fixed salary on a regular basis without having to work a specific number of hours. This compensation plan is typical of professional work, management, and occupational specialties.
In comparison to those workers who are paid by the hour, salaried employees tend to receive more predictable income, have access to benefits, and have a greater level of job security. Nonetheless, demands related to the working hours and duties may be more.
In this guide, we will discuss what a salaried worker is, who can be classified as a salaried worker, the typical salaried jobs, advantages, and how this type of worker is different from an hourly worker.
What is a Salaried Employee?
A salaried employee is a worker who gets a fixed amount of salary, usually monthly or biweekly, irrespective of the number of hours worked. The amount of salary is determined in the employment agreement, and it will not change until it is officially modified.
Salaried workers tend to work in management, administrative, creative or special technical jobs. Its remuneration package provides financial predictability, which makes budgeting easier for both the employer and employee.
Most of the non-hourly jobs come with benefits in the form of health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave. Salaried arrangements are appreciated by employers since they make it easier to manage the payroll and motivate long-term retention.
A profession that is salaried is usually characterised by performance-based bonuses, training advances, and the ability to work in a flexible environment. This method is based on rewarding the number of years worked as opposed to doing the job.
Who Qualifies as a Salaried Employee?
A salaried employee is typically someone who is paid a fixed amount on a regular basis, regardless of the exact number of hours worked. These employees often have defined responsibilities, specialized skills, and positions that require decision-making authority or ongoing oversight.
Salaried positions can include managers, supervisors, engineers, accountants, teachers, healthcare professionals, IT specialists, marketing executives, and administrative officers. These roles usually involve consistent duties that go beyond hourly tasks and require a higher level of accountability.
In most organizations, salaried employees:
- Receive a predetermined wage outlined in their employment contract. They are not paid based on the number of hours worked but rather for fulfilling their role.
- May be classified as exempt or non-exempt under labor laws, depending on their job duties.
- They are expected to contribute strategically to the organization’s objectives.
Legal guidelines in many countries specify which positions qualify for salaried status, considering factors like job description, pay scale, and the level of autonomy in decision-making.
What Are the Common Types of Salaried Employment?
Exempt vs Non-Exempt Salaried Employees
| Aspect | Exempt Salaried Employees | Non-Exempt Salaried Employees |
|---|
Full-Time vs Part-Time Salaried Employees
| Aspect | Full-Time Salaried Employees | Part-Time Salaried Employees |
|---|
Contract vs Fixed-Term Salaried Employees
| Aspect | Contract Salaried Employees | Fixed-Term Salaried Employees |
|---|
What Are the Key Benefits of a Salaried Employee?
A salary-based arrangement has a number of benefits to the individual and the company. This pay structure offers benefits in the long term over and above the monthly remuneration, as it is more predictable and offers increased career opportunities.
1. Stability and Foreseeability in Finance
A fixed, predictable paycheck is one of the largest benefits to a salaried individual. The income is constant no matter how the hours change weekly, and this assists with budgeting, planning, spending, and obtaining loans or mortgages. This steadiness is a significant factor that makes most professionals opt to take a salaried occupation rather than an hourly one.
2. Complete Package of Benefits
A salaried worker is likely to receive various benefits, including health insurance, retirement schemes, paid time off (PTO), and performance incentives. Such advantages bring new values not only in terms of money but also in terms of job satisfaction and general well-being.
3. Opportunities for Career Advancement
Most of the salaried jobs also come with increased responsibility that exposes one to promotions, professional training, and leadership. Salaried employees are frequently developed and treated as long-term assets by employers.
4. Workplace Flexibility
Even though it is possible that the salaried positions require more working hours, the flexibility of the schedule and the possibility to concentrate on the output instead of clocking in and out is frequently possible. This is something that can enhance the work-life balance .
5. Job Security and Employer Loyalty
Research has shown that employers consider salaried jobs more permanent with higher job security than many hourly jobs. This is a long-term strategy that promotes loyalty and a better relationship between employer and employee.
Comprehensively, the salaried employee gets the best of both worlds in financial stability, career development, and work benefits, and thus, this system is favorable among career-oriented people.
How Does a Salaried Employee Differ From an Hourly Employee?
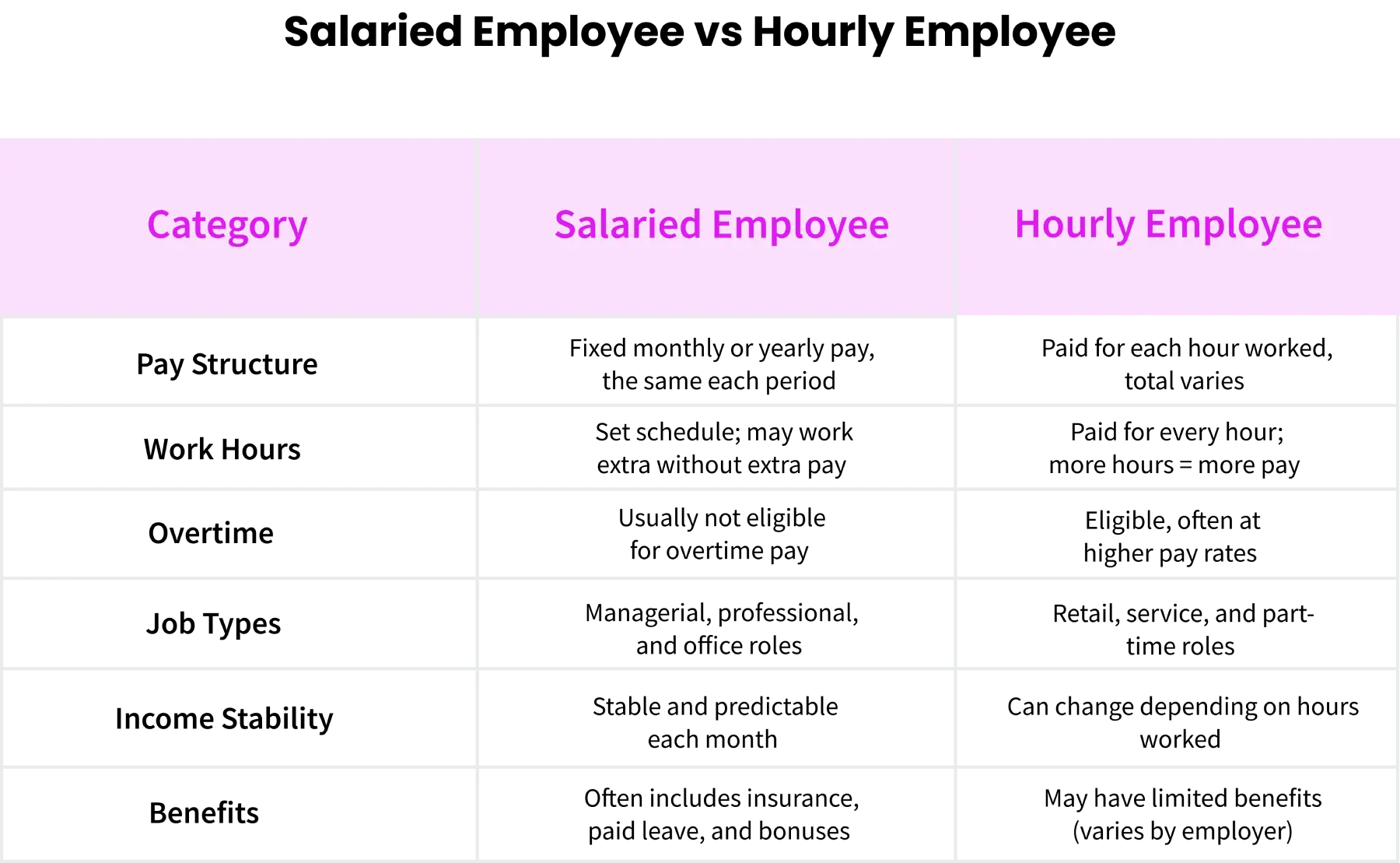
A salary earner is paid a certain amount irrespective of the number of hours spent, but an hourly employee is paid on an hourly basis. Salaried positions can have flexible hours , as well as needing to provide extra unpaid hours to meet a deadline or goal. Hourly employees, in contrast, earn overtime pay when they work more hours, but their schedule might not be as predictable.

