Home / F / Formal Organization
Formal Organization: Definition, Pros, Cons & Examples
The structure of any enterprising organization is held together by a formal organization. It outlines roles, responsibilities, and power in an organization so that work moves methodically and effectively. In the absence of hierarchy, large-scale operations would find it hard to organize and work toward achieving objectives.
Formal organizations have well-established hierarchies in business, government, or education. They possess formal channels of communication, files of procedures, and established lines of authority. This structure gives a sense of orderliness, responsibility, and direction among members.
This blog will discuss the nature of formal organization, the features, characteristics, real-world examples, advantages, and disadvantages of formal organization as compared to informal organization.
What is a Formal Organization?
Formal organization is a structured arrangement of jobs, roles, responsibilities, and power to satisfy the specific objective through coordinated efforts and formal lines of communication. It functions based on written rules, policies, and procedures.
According to a study by the Harvard Business Review, 90% of successful large companies, they rely on clearly defined formal structures to manage internal processes and communication.
The primary reason behind the existence of a formal organization is to simplify the decision-making process, decrease uncertainty, and create accountability. It makes every member aware of their responsibility and to whom they are answerable.
The significance of formal organizations lies in the fact that they assist in enforcing discipline, effective utilization of resources, and facilitating performance. They further present a model of expansion, and expanding operations becomes easier without losing control and quality.
What Are the Different Types of Formal Organizations?
There are various forms of structure that formal organizations may adopt, based on size, objectives, and industry needs. All of them differ in defining the flow of authority, patterns of communication, and distribution of roles, yet each of them is based on a transparent and rule-based structure.
1. Line Organization: This is the simplest organizational structure of authority, where the top management transfers authority in a straight row to the lower employees. It is usable in small businesses or even in the military, as it is clear.
2. Functional Organization: In this, work is also segregated according to function, such as finance, marketing, or operations. Every individual is heading a task that is of an expert subject, making them efficient.
3. Line and Staff Organization: This integrates a combination of line authority and staff roles, which are advisory as well. Decisions are processed by line managers, and guidance is given by staff experts.
4. Project Organization: There is the formation of temporary teams for specific projects. After this is done, members are back to their initial positions. That has been typical in construction, IT, and research industries.
What Are the Characteristics of a Formal Organization?
The features of formal organization are of a structured and target-oriented character. These characteristics distinguish it from informal networks and make it effective in the realization of goals.
- Clear Hierarchy: A formal organization has a well-defined structure where each role and level of authority is clearly established. Every employee knows their reporting line and responsibilities, ensuring accountability.
- Formal Channels of Communication: Information flows through established and official routes, minimizing the risk of miscommunication. These channels ensure that messages are accurate, consistent, and reach the right person at the right time.
- Rule-Governed Operations: All activities are carried out according to written policies, rules, and standard procedures. This consistency makes processes predictable, fair, and transparent for all employees.
- Goal Orientation: In a formal organization, all roles, responsibilities, and activities are aligned toward achieving defined organizational objectives. This focus ensures that resources are used efficiently, and employees work collectively toward the same targets.
What Are the Key Features of Formal Organization?
The characteristics of formal organization explain its fundamental aspects that render the formal organization structured, systematic, and effective.
- Hierarchical Structure: The power is allocated at levels, and this makes a clear flow of reporting from top to bottom. Gartner reports that 85% of large enterprises use multi-level hierarchies to ensure accountability and role clarity.
- Specialization of Work: In a formal organization, tasks are assigned based on employees’ skills and expertise. This targeted allocation allows individuals to focus on areas where they excel, boosting efficiency and productivity. Leveraging specialized skills improves work quality and helps the organization achieve better outcomes in less time.
- Specified Accountability: Each employee is clearly assigned responsibilities and held accountable for their work. This ensures tasks are completed efficiently, and any issues can be traced to their source. The system promotes discipline, transparency, and reliability while motivating employees to maintain high performance standards .
- Operational Stability: A formal organization is structured to run smoothly even during staff changes. With roles, duties, and reporting lines predefined, replacements integrate with minimal disruption. This stability supports long-term planning, consistent performance, and adaptation to changes without affecting overall efficiency.
What is an Example of a Formal Organization?
There are both formal organizations in the public and private sectors. They do so under written regulations, authoritative power, and formal processes.
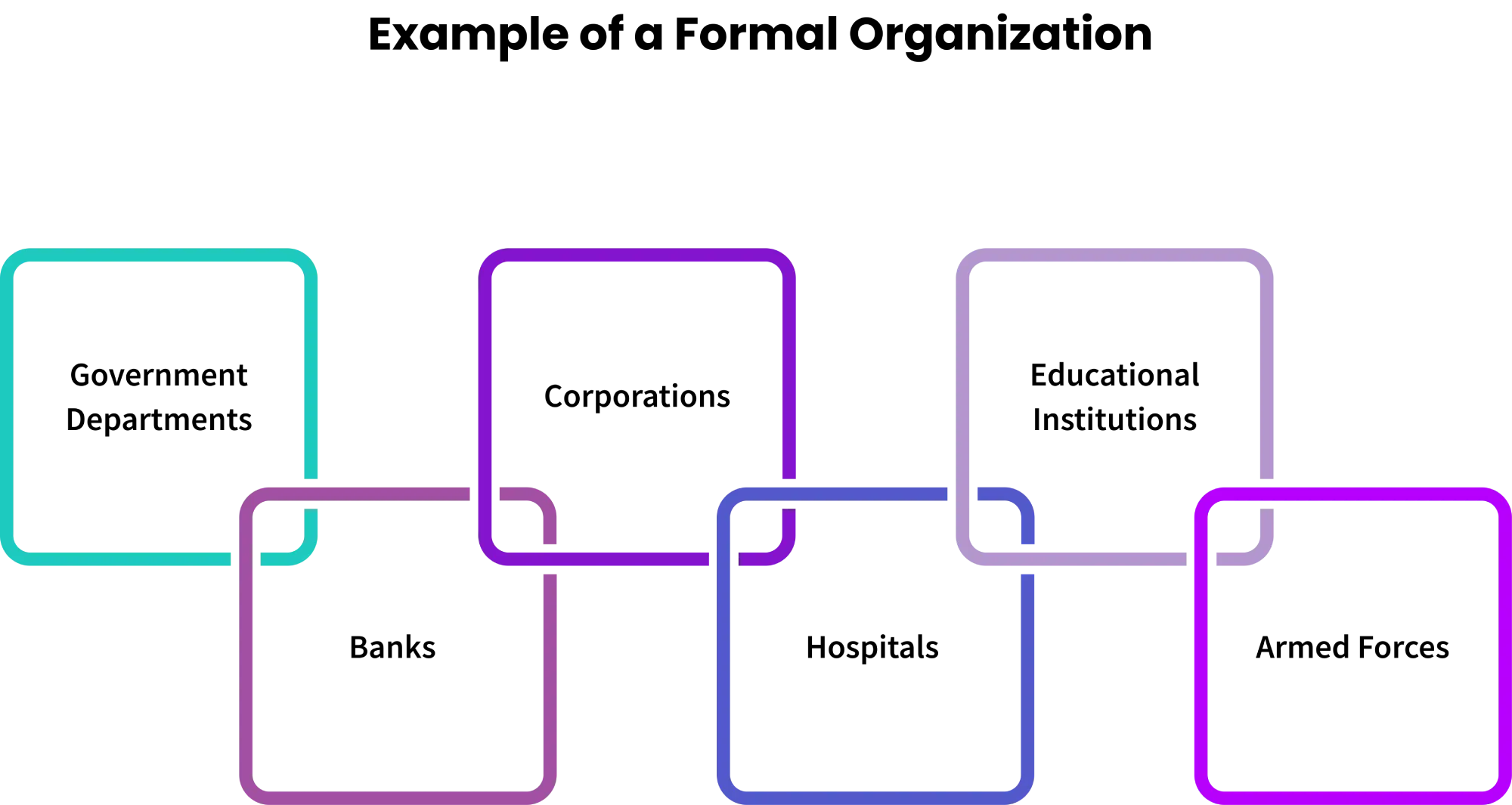
- Government Departments: Offices like the Department of Health or Education follow strict rules, regulations, and structured reporting systems. This ensures efficient functioning and accountability at every level.
- Corporations: Large companies such as Microsoft or Toyota operate with fixed roles, policies, and accountability systems. These structures help maintain organized and consistent operations across departments.
- Educational Institutions: Schools, colleges, and universities work under formal rules and clearly defined duties for both staff and students. This ensures discipline and smooth academic operations.
- Banks: Financial institutions like SBI or HDFC Bank follow standard policies, defined roles, and strict regulatory guidelines. This structure ensures compliance and reliable financial services.
- Hospitals: Public and private hospitals adhere to established protocols, roles, and responsibilities. This enables them to deliver healthcare in an organized and efficient manner.
- Armed Forces: The military operates under a strict command structure, with clearly defined ranks, duties, and responsibilities. This ensures discipline and operational effectiveness.
What Are the Advantages of Formal Organizations?
The benefits of formal organization are characterized by the fact that it has a systematic and disciplined system of managing work.
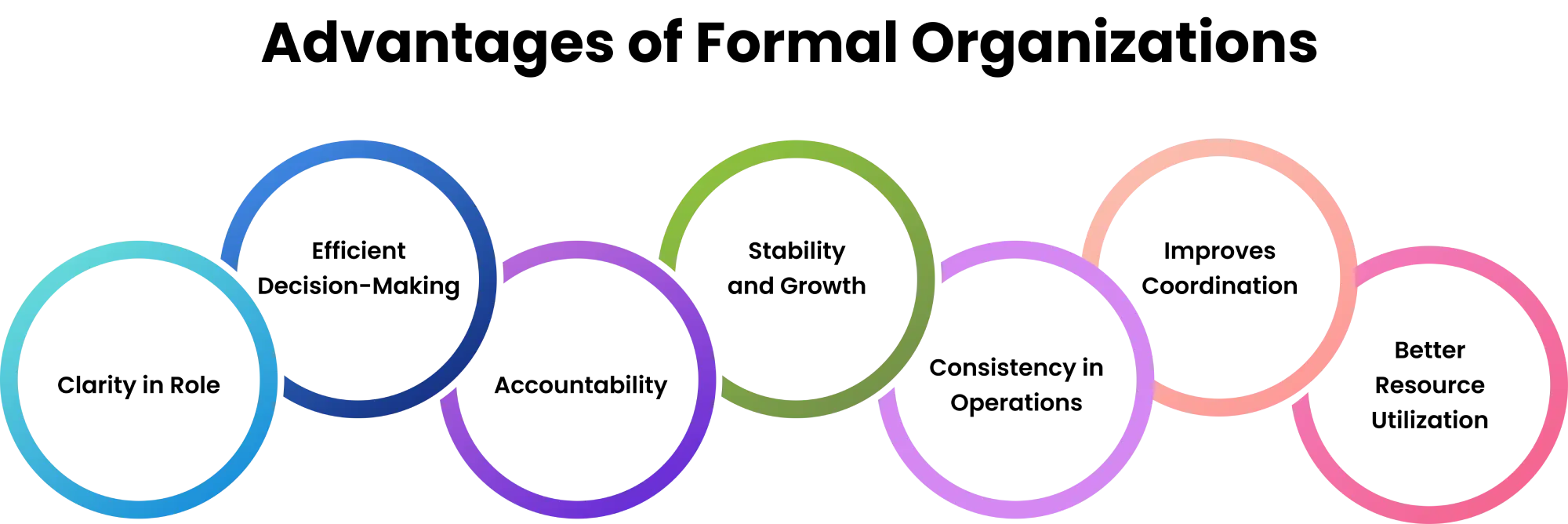
- Clarity in Role: All employees have a clear understanding of their responsibilities and position in the hierarchy. This reduces overlap of work, prevents confusion, and ensures that everyone knows what is expected of them.
- Efficient Decision-Making: Decisions are taken at the right level within the chain of command, which speeds up processes. This structured flow ensures that instructions are precise, and authority is respected.
- Accountability: Employees can be held responsible for their actions, as tasks and duties are clearly defined. This improves discipline, quality control, and overall work performance.
- Stability and Growth: A formal organization offers long-term stability by following established systems and processes. This allows the business to expand without losing operational control.
- Consistency in Operations: Standardized procedures ensure that work is performed in a uniform and predictable manner across all departments. This consistency maintains quality standards and helps in reducing errors, improving efficiency, and ensuring that employees follow the same processes.
- Improves Coordination: Clearly defined reporting lines and established communication channels make it easier for employees to share information and collaborate effectively. This structure enhances teamwork, reduces misunderstandings, and ensures that all members are aligned toward shared objectives.
- Better Resource Utilization: With tasks allocated systematically, manpower and other resources are used more efficiently, reducing wastage and maximizing productivity.
What Are the Disadvantages of Formal Organizations?
Although useful, a formal organization also has drawbacks that can influence flexibility and the morale of employees.
- Rigidity: A Gallup survey showed that rigid work environments lead to a 31% drop in employee engagement. This can be done at the expense of creativity and dynamics because of being rigid with rules.
- Slow Communication: In a formal organization, information often travels through multiple hierarchical levels before reaching its destination. This can result in delays, misinterpretations, or lost urgency, especially when quick decisions are needed for operational efficiency.
- Employee Dissatisfaction: Limited flexibility in job roles, along with strict compliance with regulations, can cause frustration among employees. Over time, this dissatisfaction may lead to reduced morale, lower productivity , and increased employee turnover rates.
- Increases Administrative Costs: Maintaining detailed records, compliance documents, and procedural guidelines requires significant resources. The need for extensive documentation and monitoring systems can increase operational expenses, especially in large organizations with complex processes.
What is the Difference Between Formal and Informal Organization?
A formal organization is characterized by a set of rules, oriented toward goals, whereas an informal organization is naturally developed based on interpersonal relations in the workplace.
Knowing the difference will help you choose the right method for your business. So, look at it in detail: